Continuous Integration and Deployment with GitHub, Travis CI, Sauce Labs & Heroku

Continuous Integration tool Travis CI seemlessly integrates with GitHub, Sauce Labs & Heroku to automate building, testing and deployment - critical steps to automate web application development and improve productivity!
After several unsuccessful attempts to automate build, test and deployment tasks for Ask GitHub I stumbled on Sam Saccone’s blog post. I got inspired to try again. Few hours latter I had a working solution!
This blog post deep dives into the Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) configuration and setup for Ask GitHub.
“Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early” Source:ThoughtWorks
“Continuous deployment can be thought of as an extension of continuous integration, aiming at minimizing lead time, the time elapsed between development writing one new line of code and this new code being used by live users, in production.” Source Agile Alliance
Architecture
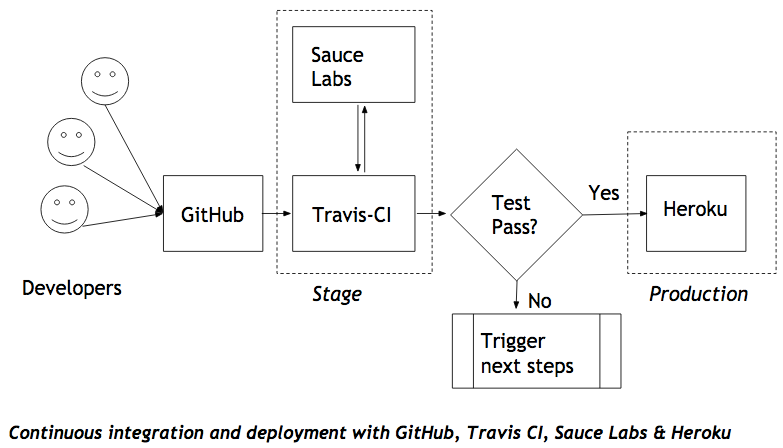
Workflow
- Developers are pushing code changes to GitHub
- Application is built and deployed on a fresh staging environment by Travis CI
- Selenium test cases are run remotely on a fresh instance with developer defined OS & browser by Sauce Labs
- Status of test cases are passed back to Travis CI
- If all the test cases pass the code is automatically deployed on Heroku
Check List
- Code on GitHub public repository
- Additional steps are required for private repository
- Create a Travis CI account (you can use your GitHub account)
- Create a Sauce Labs account(you can use your GitHub account)
- Visit Travis CI integration page
- Provide your GitHub repository name
- You will be provided a code block for
.travis.ymlfile and access tokens
- run
travis setup herokuto generate theapi_keyfor.travis.yml - Selenium test script with test cases
Step 1:
- Add
.travis.ymlfile at the root of your repository to tell Travis CI what to build - AskGitHub .travis.yml
.travis.yml
- Lines 1-3: Provide the language and version for build
- Lines 4-7: Code block from Sauce Labs
- Lines 8-9: Sauce Labs addons
- Lines 10-14: Build information
requirements.txtprovides a list of dependency modulespython RunFlask.py worker.py &starts the newly build web application in the background
- Line 15: Test script location
- Lines 16-18: Rule to build and test only on
masterbranch - Lines 19-23: Steps to deploy on Heroku after test pass
Step 2:
- Configure Selenium test script to work remotely on Sauce Labs VM
- AskGitHub travis-testcases.py
travis-testcases.py- Lines 9 - 30: Initial setup
- Lines 11 - 19: Setup to remotely test on Sauce Labs
- Lines 23 - 24: Remote driver
- Line 27: URL for testing
- Line 29: Default test result
- Line 20: Store messages
- Line 32 - 62: Selenium test cases
- Lines 34 - 38: Change test result status if test case fails
- Lines 65 - 72: Clean up and status update
- Lines 67 - 68: Print URL of job
- Line 71: Update test result status. Status of the test result determines if the build is deployed!
- Lines 9 - 30: Initial setup
- Add badges to
README.md
Step 3:
- Login to Travis CI
- Add you GitHub repository
- Set environment variables for your repository
SauceLoginSauceAccessKeyPORT
Step 4:
- Commit
.travis.ymlandtravis-testcases.pyto GitHub
Step 5:
- Visit Travis-CI and select your repository
- watch the build and test log
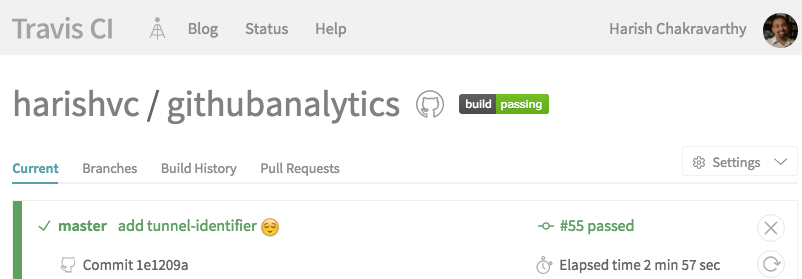
- watch the build and test log
- Visit Sauce Labs and click on your build
- watch the video of the test!
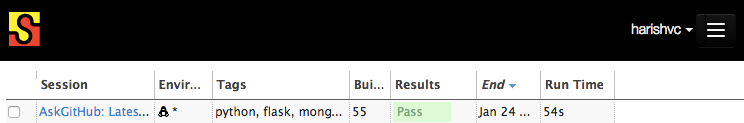
- watch the video of the test!
- Visit
README.mdto view the status of test cases

Observations
- Travis-CI provide fresh staging environment with hooks to test and deploy
- Sauce Labs comes to the rescue when you need to test on real browsers
Related Articles
- Testing in a real browser with Sauce Labs with Travis CI
- Travis CI & Heroku
- Continuous Deployment
- Continuous Integration is Dead
- Continuous Delivery Vs. Continuous Deployment: What’s the Diff?
Tags
- Continuous Integration
- Continuous Deployment
- Travis CI
- SauceLabs
- GitHub
- Selenium
 Harish Chakravarthy is an intrapreneur leveraging technology to make a positive difference.
Interests include API integration, user experience, data visualization and analytics.
Harish Chakravarthy is an intrapreneur leveraging technology to make a positive difference.
Interests include API integration, user experience, data visualization and analytics.